Home » Articles posted by Travis Oliver (Page 2)
Author Archives: Travis Oliver
How to Eliminate a Pest
Pests can cause many problems, including destruction of crops and damage to homes. They may also spread disease. Some common pests include mice, roaches and fleas.
Physical barriers can be used to block pests from entering a property or garden. These can include removing their food, water and shelter sources. Contact Nature Shield Pest Solutions now!

Pest identification is the first step in a pest control plan. It includes looking for a variety of clues to determine what the pest is and the damage it is causing. It also involves understanding the pest’s biology, including its life cycle, habitat and food sources. This information helps map out an integrated pest management (IPM) plan that eliminates the pest without harmful chemicals or disruption to beneficial organisms.
The morphological characteristics of a pest, such as the structure of its mouthparts or wings and antennae help with identifying it. The location and type of damage to a plant can also aid in determining the pest involved. The sex or stage of the insect also plays an important role in determining which control tactics are used. For example, caterpillars of many butterflies and moths feed on specific types of plants, while larvae or adult beetles consume leaves, fruit, roots or other parts of a plant.
Most pests have certain windows of vulnerability or “windows of opportunity” when they are most susceptible to control. This can depend on the pest species, as well as time of year and other factors. For example, weeds are easiest to control in their seedling or mature stages, while insects may be most easily controlled during immature or egg-laying stages.
Regular scouting and monitoring can help identify pest problems before they become severe. This can also be done with the assistance of a pest identification guide. These guides provide pictures that can be compared to the pest to identify it, and offer helpful information about the pest’s habits, habitat, threats and control measures.
For home pests, the most effective way to prevent infestation is to keep it from occurring in the first place. For instance, rodents can be kept away from homes by sealing cracks and crevices, cleaning garbage cans on a regular basis and removing clutter from the house. Insects can be prevented from entering the home by keeping the lawn mowed and free of debris, and storing books and papers in plastic bags or cardboard boxes.
In addition, pests can be prevented from breeding indoors by locating and eliminating their breeding sites. These can include dead animals in attics or chimneys, pet feces outside and in garbage cans, overgrown shrubbery and trees providing shelter to mice, ants and other insects, as well as unclean garbage cans.
Pest Prevention
The best way to reduce pest problems is through preventive methods. Generally, these are cheaper and more environmentally friendly than extermination techniques. However, prevention requires a team effort between facility management and the pest management professional. This includes identifying what each is responsible for and making sure they both are doing their job. This can include setting up an inspection protocol for incoming shipments to avoid bringing in pests or assigning someone on staff to regularly inspect locker rooms for flies and cockroaches. Other preventive measures may include installing door sweeps, sealing expansion joints and locating dumpsters away from entrances to reduce moisture attracting pests like rodents.
Even if a building is kept very clean and sanitary, it is still possible for pests to establish themselves in large enough numbers to cause damage or health problems for occupants. For example, bird droppings can cause serious damage to structures and pose a health risk when inhaled. In addition, some birds are known to carry diseases such as salmonellosis.
Ideally, the goal of any pest control program is to prevent infestations from occurring at all. However, it is very difficult to eliminate every last pest from a building. Even the most pristine facilities often have dozens of imperceptible cracks and crevices both inside and out where pests can enter and hide.
Prevention tactics are used in combination with sanitation and pest barriers to achieve maximum efficacy. For example, it is important to keep crumbs and spills cleaned up and to store food in airtight containers. Garbage cans should be kept tightly closed and emptied regularly. Also, clutter should be minimized both inside and outside to provide fewer hiding places for pests.
Some pests, such as ants and spiders, can be managed with traps or baits alone. However, cockroaches require insecticide sprays. Integrated pest management (IPM) uses a combination of methods to manage pests and protect people, animals and plants without using toxic chemicals. Depending on the type of pest, IPM can include monitoring, habitat modification, physical controls, cultural practices and biological control. Biological controls are any method that involves the use of a pest’s natural enemies or parasites to control it, including predators, pathogens or competitors.
Pest Control Methods
There are many ways to control pests that do not involve the use of chemicals. These methods are called physical, mechanical or biological controls and include trapping, barriers, fences, netting and decoys. Heat, radiation and electricity sometimes can be used to alter the environment of a pest. Biological controls include introducing natural enemies of the pest, such as predators, parasites or pathogens. The natural enemy may be native to the area, or it may be brought in from another location. This method of controlling pests requires extensive research into the biology of the pest and its natural enemies. It also involves careful timing to avoid disrupting the enemy population and to ensure the new natural enemies will be successful.
Chemical control is a quicker way to reduce a pest population. Examples of chemical controls include sprays, repellents and insecticides. However, it is important to note that the chemical used should be environmentally safe and should not harm non-target organisms.
In IPM, pesticides are used sparingly, only when the pest numbers are high enough to warrant treatment. The goal is to keep the number of pests below the level that would cause unacceptable damage.
Physical and biological pest controls are preferable to using toxic chemicals. However, they take time and effort to implement. Some physical and biological methods require scouting to find pests and monitor their numbers and damage. For example, if you know that a pest species likes to lay its eggs in damp soil, you can place a bait station where the pests are likely to be.
It is also helpful to have a plan for dealing with the pests once they are found. Scouting and monitoring will help you determine when the pest populations reach threshold levels. Scouting and monitoring also provides valuable information about the pests, such as their feeding habits or their damage to plants. For example, if you know that red weaver ants feed on snails, you can use this knowledge to create an effective trap for these insects. Also, if you can see where the pests are traveling in your yard, such as their preferred route through it, you can block off that route and make it more difficult for them to move between locations.
Pesticides
The term pesticide is any substance that kills or prevents pests (insects, mice, other animals, unwanted plants, weeds, fungi, bacteria and viruses). Pesticides can be anything from chemicals to natural substances such as animal waste, plant extracts, minerals and microbes. They are formulated into liquids, gases or powders to be spread on crops, trees or plants, or sprayed or dripped onto the surface of soil, water or other surfaces.
Pesticides are generally considered to be dangerous to people and animals if they come into direct contact with them. However, if you are careful when applying pesticides and follow the manufacturer’s instructions, you can reduce any risks to health or the environment.
Most pesticides are designed to only affect their target organism. However, if other insects or animals accidentally ingest the pesticide or come into direct contact with it, they may be harmed. To reduce the risk of harm to non-target organisms, always use the lowest amount of pesticide that will still provide adequate control.
The use of pesticides is regulated at the federal, provincial and territorial levels through various acts, regulations, guidelines, directives and bylaws. Provincial and territorial governments are also responsible for licensing applicators, vendors and growers, as well as responding to pesticide spills or incidents.
Before a pesticide can be sold or used on food crops, it must first pass through an extensive testing process. The testing includes screening against a wide range of organisms and determining whether it is safe for humans, other animals, plants and the environment. It must also meet a safety level set by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) that is far lower than any residues that could pose a threat to human health.
When a pesticide is approved for use, it is issued a permit that states the maximum allowable residues on food crops. The CFIA samples and tests foods for residues, which are typically found in the highest concentration on grains, fruits and vegetables. If a crop is contaminated above the permitted residue level, the producer is required to take corrective action.
Biological and organic pesticides are made from things found in nature or derived from natural sources, such as microbes or natural substances like copper or sulphur. They do not contain synthetic chemicals and are approved for use on organic crops.
Things to Keep in Mind Before You Start a Kitchen Remodeling Project
A well-renovated kitchen boosts a home’s value and livability. It also makes for a more pleasant cooking experience, and can make it easier to entertain guests.
The first step is determining your goals for the remodel. Whether you’re simply upgrading worn surfaces and materials, adding new features to enhance livability or increasing your resale potential, your motivation will guide the rest of your project.

If you’re tired of tripping over old linoleum flooring or struggling to make room for all those baby bottles, it may be time to consider a kitchen home improvement project. A kitchen remodel can give you the functional space you need while adding value to your property. But before you jump in feet first, there are a few things to keep in mind.
Start by developing a realistic budget for your project. This should include a breakdown of all the costs, including materials and labor. Having an idea of what your project will cost can help you avoid any surprises down the road, and ensure that the renovation is completed to your satisfaction.
Once you have your budget in place, it’s important to stick to it. If you overspend on a big ticket item, it could impact the rest of the project. It’s also important to set a timeline for the project. This will give your contractors a deadline and help to keep the renovation on schedule.
It’s also a good idea to think about how you will use your kitchen during the remodel, and plan accordingly. It’s likely that you will not have access to your kitchen during the demolition and build phase of the project, so be prepared to eat out or prepare meals in another part of the house. If you’re planning on purchasing new appliances, be sure to order them well in advance. Oftentimes, they take a long time to arrive, and you don’t want to be stuck without an oven while the renovation is underway.
Unless you’re going for a complete gut renovation, it’s best to stay within the kitchen’s current footprint. Moving plumbing lines or electrical wiring is a major expense that can quickly add up. It’s also a good idea to leave the existing sink and dishwasher in their original locations, since this is where they are best positioned for functionality.
It’s a good idea to have a general contractor handle the construction aspect of your kitchen remodel. They will be able to recommend subcontractors for any specialty work needed, and will know how long certain tasks should take based on their experience with similar projects. However, if you have construction experience, it can be more cost effective to act as your own general contractor and manage the project yourself.
Designing
As one of the most frequently performed home renovations, redoing the kitchen offers a wealth of possibilities. These include enlarging the room, reconfiguring the layout, or upgrading the appliances and fixtures. The first step in the process is to determine the scope of work. This will give you a clear idea of what to expect when meeting with designers and contractors, and what kind of budget you need to get the job done right.
The kitchen is a gathering place for family and friends, so it’s important to design it with sociability in mind. Comfortable seating, a large table surface area, and an open layout with a kitchen island are all great ways to encourage comradery. A glamorous kitchen will also have plenty of light, which can make any space feel bigger.
A good way to start your kitchen remodel design is by brainstorming what you want the space to look like. You can draw your own floorplan, or consult with a designer or contractor to help you visualize the finished product. A big part of this step is deciding what materials you want to use, and how you want the design to flow.
One of the most common mistakes homeowners make when remodeling their kitchens is choosing a color scheme that’s too dark. Dark colors shrink a room and can make it feel closed-in and unwelcoming. White or off-white finishes open up a space and make it feel more welcoming. A good design will also incorporate plenty of lighting, including task and under-cabinet options.
There are a lot of different types of counter-tops, cabinets, and flooring, so it’s important to weigh your options carefully before making a decision. Consider durability, cost, and maintenance in addition to aesthetics when comparing your options.
When you’re ready to start shopping for supplies, consider a design-build firm that combines professional kitchen remodeling services with interior design. This can streamline the process and save you time and money. It also means you’ll be working with the same company from the start of your kitchen remodel to the finish line, which can help keep your project on track and within budget.
Budgeting
It’s important to know how your kitchen remodel budget will break down so that you can avoid the costly surprises that often pop up on renovation projects. Labor costs typically eat up 20 to 35 percent of your overall project cost, and cabinets can eat up another big chunk. To combat these unexpected expenses, experts recommend setting aside 20 percent of your renovation costs for surprise discoveries. These could include water damage or electric that isn’t up to code.
It may help to make a list of your must-haves and want-to-haves, so that you can prioritize each item. It’s not worth sacrificing the functionality of your kitchen by skimping on appliances, for instance, and you should also resist the temptation to go overboard on luxury items. Instead, save money by choosing cheaper materials and fixtures for the elements that matter most, such as a new sink or dishwasher, and splurge on something like a built-in wine fridge or warming drawer when your budget allows it.
Once you’ve made a plan and budget, stick to it as much as possible. It’s easy to get tempted by “that would be so cool if we added…” as the project unfolds, but that’s how kitchen remodeling projects get out of control. Adding extras will quickly inflate your budget and can derail the entire project.
To keep your kitchen remodeling budget in check, consider hiring an owner/operator contractor rather than a general contractor. These independent contractors have lower overhead and don’t charge a commission for their services, so they can offer you more competitive rates. They also have a network of subcontractors they work with regularly and will negotiate discounts on your behalf. If you’re able to handle some of the remodeling yourself, that will also cut your costs significantly. For example, you can save on demolition fees by handling the task yourself, and you can save money on kitchen supplies by shopping around for better deals. Another way to keep your costs down is to find out if there are any local discounts or rebates on appliances, kitchen fixtures and other items you need.
Choosing a Contractor
The kitchen is the heart of the home, and its transformation into a gorgeous space not only adds value to your property but also boosts household comfort and functionality. But before your kitchen remodel vision becomes a reality, you need to find the right contractor to bring it to life. This pivotal decision will have a significant impact on your contentment with the finished product and the returns you receive on your investment.
Start your search by asking friends, family, and coworkers for referrals. They may be able to provide insights into the contractor’s reliability, work ethic, and professionalism that you won’t be able to find online. Once you’ve compiled a list of potential contractors, begin evaluating them by checking their licensing and insurance. You can also assess their experience and expertise by reviewing their portfolio of previous kitchen remodeling projects. Look for before-and-after pictures to gauge the quality of their work and style compatibility with your vision.
You should also ask potential contractors about the timeline of their projects. It’s important to have a clear understanding of how long your kitchen will be out of commission and how much time you should expect for the research and planning, demolition, construction, and finishing touches. Be wary of any contractors who cannot give you specific time frames or of those who promise a timeline that seems unrealistically fast.
Reputable kitchen remodelers will be able to explain their processes and provide you with a realistic projection of how long your project will take. They should be able to tell you how much of their team will work on your project as well as any subcontractors they plan to use. You should always request the names and contact information of anyone they plan to use, and Google them just as you did for the primary contractors in your search.
Lastly, you should ask potential contractors about their project management strategies. This includes how they will keep you updated on progress, any issues that arise during the remodel, and how they will handle change orders. It is important to understand that unforeseen challenges will almost certainly come up during any project, and you should choose a contractor who has a solid process for keeping you in the loop and communicating with you throughout these hiccups.
Septic Tank Regulations – Legal Requirements For Proper Maintenance
In most states, septic tank professionals must complete specific training courses and pass a certification exam to be able to design or install septic systems. These certifications ensure that the system is designed and installed to meet state regulations and protect environmental resources.
Regulations often stipulate minimum separation distances from septic tanks to residences, wells, and property lines. Check Septic Tank Services Near Me and your local health or environmental department for specific requirements in your area.
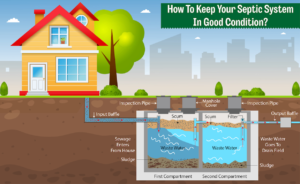
The septic tank is the first step in an onsite wastewater treatment system. The tank collects and stores sewage from the home, separating solid waste from the liquid effluent. Solids that sink to the bottom of the tank become sludge, while scum rises to the surface of the wastewater and floats on top of the liquid waste. The liquid effluent exits the septic tank through a perforated pipe that connects to an absorption field, or leach field.
The septic tank must have adequate capacity to handle the expected load of wastewater from the house, including laundry and garbage disposal waste. The design should take into account the number of bedrooms in the household and any expansion attics. The flow rate and volume of solids in the wastewater will also factor into the septic tank’s capacity.
A septic tank should be constructed from durable materials that are resistant to corrosion, decay, and frost damage. The tank should also be water-tight, and all joints below the liquid level must be sealed and tested.
When a new septic tank is installed, the outlet connections of the tank and each compartment thereof must be provided with either a tee not less than four inches in diameter or a durable baffle. The baffle or tee must be permanently fastened in place and extend below the liquid level by 25 to 40 percent of the total liquid depth.
The septic system must be installed on a site that is free of water and gravel runoff and soil conditions that could cause erosion and movement of the tank or its components. It is recommended that a site evaluation be performed before construction.
It is also important to map out the septic tank and the drain field or mark the location with permanent stakes. This will help homeowners identify and avoid the septic system when working on landscaping, paving, or any other work that may disturb the tank and drain field. It will also help prevent the accidental or intentional damage of septic system components.
Once the septic tank is installed, it is important to backfill the area around the tank and drain the field with soil that will not settle over time. The backfill should be free of clods, large rocks, and frozen matter, and must be amended with crushed rock or pea gravel no smaller than 1/2-inch in size if native material is not suitable.
Maintenance
A septic system requires regular maintenance and responsible operation to preserve its integrity and protect the environment. The state takes this seriously and has strict regulations regarding the design, installation, and management of septic systems to minimize environmental impacts and public health concerns.
All septic tanks have an opening that waste flows through, known as the outlet. A septic tank’s lid is usually secured by a grate to prevent animals or children from entering the septic system and may be locked to discourage tampering. The tank walls must be constructed of strong materials to resist the flow of septic liquid effluent. A septic tank should be pumped regularly to remove solid waste accumulations that are not biodegradable. This is especially important since septic tanks cannot remove all of the wastewater solids that enter the tank, regardless of how well the system operates.
Typically, the septic tank has a PVC “T”-shaped fitting with a short section of horizontal piping leading into a slightly longer vertical section. The bottom of the vertical section must extend several inches below the scum layer. The liquid waste in the septic tank is forced through this outlet to a distribution box or an absorption field for continued treatment.
The distribution box contains perforated pipes that distribute the liquid waste from the septic tank evenly throughout a drain field or seepage pits. The distribution box and the absorption field or seepage pits must be properly sized and constructed to ensure that the system functions correctly and does not pose a risk of environmental pollution.
Besides proper system construction, the maintenance of a septic system includes regular inspection by a professional inspector. These inspections are necessary to check for the proper functioning of the septic system and to detect any potential problems, such as clogging or leaks. Inspectors should look for signs of sludge buildup in the septic tank and ensure that the absorption fields or seepage pits are adequately sized and located to avoid contamination of groundwater or nearby surface water bodies.
Inspection
If you own a home with a septic system, it’s important to stay on top of inspections and certification. This not only ensures that the septic tank, drainfield, and leach field are safe, but also helps keep your home’s value up.
Generally, inspectors will check three elements of the septic system: the septic tank, the distribution box, and the leach field. They’ll look at the septic tank to make sure there are no cracks, leaks, or structural problems and that it isn’t too full or too empty. They’ll also look at the leach field to see if it is well-spaced and properly sized, and that there are no clogs or leaks.
A septic tank must be inspected every two to three years. When your septic tank needs to be pumped, it’s a good idea to use a licensed septage waste transporter (septic pumper). They can inspect the septic tank and determine how much material is in it. They can also help you keep a record of all the pumping and inspections and any maintenance and repairs that are required.
In addition to looking at the septic tank and its components, an inspector will check for other problems such as a soggy yard that’s wet all the time, lush vegetation, or standing water in the drainfield area, as these may indicate a septic system problem. They’ll also look at the D-box, or distribution box, for problems such as damaged outlets that restrict flow, or a tilting or tipping that causes uneven distribution of wastewater.
In the state, septic system professionals are required to pass written, oral, and practical examinations before they can be certified by the State Sanitary Code. This certification demonstrates that they have a thorough knowledge of how to design and install on-site septic systems that meet environmental protection standards, especially in ecologically sensitive areas. Homeowners should verify their septic system designers and installers are certified, and ask for recommendations and reviews before hiring them. They should also check with their local health departments to learn if there are any additional regulations governing the installation, inspection, and maintenance of on-site septic systems in their area.
Certification
Septic tank professionals must pass a rigorous exam to become licensed to install or repair septic systems. The exam covers minimum site conditions, construction criteria, appropriate connections and venting, wastewater disposal, and safety considerations. Licensed septic system professionals can help customers choose the right septic tank for their property and help them maintain their septic system to ensure proper operation and prevent potential problems.
Septic tanks are essentially settling chambers that allow time for scum and sludge to separate from wastewater, so clear liquid can flow into the drainfield or pump tank. A septic tank is typically required to have a capacity of at least 1,000 gallons for a single-family dwelling. For multiple-family homes, the tank size increases by 125 gallons for every additional bedroom.
The tank must be constructed of sound and durable materials that are resistant to corrosion, decay, or frost damage. It must also be watertight and free of cracking, leaking, or buckling due to settlement or backfilling. An inspection port that extends to the finished grade must be provided for each tank inlet and outlet, except for outlets where a baffle, septic solids retainer, or effluent filter is used. These must be directly below the manhole, and the manhole cover shall be a secure, bolted, or locked lid.
A septic tank should be located on a level, well-draining site with a suitable soil type. The septic tank should be at least six feet away from any structure and within three feet of the property line. The tank should be surrounded by a backfill that is free of large stones, roots, and other foreign objects and thoroughly tamped.
The absorption field is a series of trenches or distribution pipes that are filled with washed gravel, stone, or a graveled product where the wastewater is biologically treated by the soil. It is important to properly size and install the absorption field, as the wrong material can lead to costly repairs and system failure.
Homeowners can reduce the load on their septic system by using water efficiently, fixing leaky fixtures, and being cautious about what goes down the drains. They can also help the system work better by getting regular septic tank pumping and by having their septic system inspected by a professional, who can catch any problems early on.
Insulation Remover – How Much Does it Cost to Remove Old Insulation?
Replacing old insulation can be a very effective way to make your home or business more energy efficient. However, removing the old insulation can be a messy and time-consuming project.
Whether you’re a DIYer or hiring a professional, there are several things to consider when it comes to tackling this task. For more information, click the Perth Insulation Remover to proceed.

Insulation is vital for energy efficiency in both homes and businesses. However, it can become damaged by pest infestations, moisture damage, and general wear and tear over time. When this happens, it’s important to remove and replace the insulation. This will improve energy efficiency and prevent health risks.
Before beginning the removal process, it’s crucial to clear the work area of furniture and other objects that could be in the way. This will prevent injuries and make the process easier. You can also cover floors and surfaces with drop cloths to protect them from debris and insulation particles during the process. Lastly, you should purchase personal protective equipment (PPE) such as goggles, gloves, and a mask to protect yourself from irritation.
Depending on the type of insulation you have, there are several different ways to remove it. You can use a knife or foam saw to cut through the insulation and pull it away from the wall or ceiling, or you can use a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter. It’s recommended to wear PPE when removing old insulation, as it may contain mold spores and dust that can cause allergies.
Some types of insulation, especially spray foam, are flammable and require special handling and disposal procedures to minimize fire hazards. It’s best to hire a professional with the right credentials and equipment for this task. Additionally, some older insulation materials are contaminated with toxic substances like asbestos, which can cause respiratory problems when inhaled.
The insulation removal process is a messy and inconvenient job that requires proper safety measures to avoid injury or health problems. If you have a large project that involves changing walls, ceilings or floors, it’s a good idea to call in a professional insulation removal company. They will handle the job safely and efficiently.
Insulation can be made from a variety of materials, including fiberglass, rock and slag wool. It can also contain dangerous chemicals such as formaldehyde, asbestos, and other carcinogenic substances. The best option is to hire a professional insulation removal company that will take care of the hazardous materials and ensure that they are disposed of properly. They will also follow strict safety protocols to protect themselves and your family from exposure to harmful contaminants.
Tools
If your attic was previously insulated with Blown Cellulose or Fiberglass Batt Insulation, then a large amount of material will need to be removed from the area before new insulation can be installed. If this is the case, then it will be necessary to use a special vacuum system that will allow you to remove the old insulation without spreading it throughout your home. In addition to a professional vacuum system, you will also need some special tools to help with the process of removing insulation.
A wire stripper is a tool that can be used to remove insulation from a wire or cable. This tool generally has a pair of opposing blades that can be closed together to cut the wire or cable. It can then be used to peel the insulation off of the conductor and remove any remaining adhesive. It is recommended that you wear a face mask and gloves when using this tool.
There are a number of different types of wire strippers available on the market. The different variations differ in appearance, handle size and shape, handle coating (often rubberized to protect against electric shock), and the number and size of notches that are built into the tool. However, all of the different versions of this tool perform the same function.
To use the wire stripper, first position it on the end of a piece of wire and close the jaws around it. Then, slowly press the handles together to cut through the insulation on the wire. Be sure not to press too hard, as you could accidentally nick the metal conductors underneath.
Another type of insulation removal tool is a screwdriver-like device that has one or more screw-in prongs at the base of the handle. It is designed to pierce through the outer layer of insulation and expose the copper core. It is then possible to use a wire stripper to remove the rest of the insulation from the conductor.
This tool is designed to remove bonded insulation from medium voltage cables, including XLPE and EPR. It can be adjusted to fit a variety of wire sizes and is easy to operate.
Time
If the old insulation in your home is moldy or water-damaged, it may be a health hazard that needs to be removed. This process requires tearing down the drywall in the affected areas and disposing of the damaged materials and any contaminants that have been exposed. It is a demanding DIY project that must be performed by someone who is familiar with the process and adheres to strict safety measures.
The most common kind of insulation in homes today is blown-in fiberglass or cellulose. This is more difficult to remove than batting, but it can be done if you have the proper equipment and professional assistance. The first step is to prepare the area. Cover up any items in the living room, put down a drop cloth or plastic sheeting, and clear a path to your attic access door. You can also wear protective clothing and a dust mask to prevent inhaling any contaminants.
You’ll need a powerful insulation removal vacuum with a HEPA filter. This device will quickly suck up the contaminated materials and transport them into a large garbage bag for disposal. Make sure it has a long extension hose and can handle the volume of materials that will need to be removed. You’ll also need a sturdy ladder to reach high attic spaces safely and heavy-duty garbage bags. You should also have a partner to help you carry full bags and transport them to your vehicle for disposal.
When removing blown-in insulation, you’ll want to work in small sections. This will give you a better chance of keeping the contaminants contained to one small area rather than spreading them throughout your entire house. It will also reduce your risk of inhaling contaminated dust and mold spores.
It’s important to take your time during this process. If you rush, you could wind up with a mess that will take more time to clean up. Once you’re finished, remove the empty bags from the attic and discard them in a dumpster outside your home. Alternatively, you can use a spray foam insulation to replace the existing blown-in insulation in your walls. This is a more environmentally friendly alternative that will save you the time and hassle of tearing down your walls. It can also be completed in a day, making it less disruptive than a complete drywall teardown.
Cost
Insulation can be a major investment in your home. However, there are many benefits to having insulation installed in your home, including lowering energy bills and making your home more comfortable. In addition, you can also boost your home’s resale value. But how much does it cost to have insulation installed? The answer to this question varies depending on the type of insulation, the amount of insulation, and the installation process.
Insulation is material designed to prevent heat or sound from passing through walls and ceilings. It can be made of a variety of materials, and it is used in homes to help reduce their heating and cooling costs. There are many different types of insulation, and each one has its own unique characteristics. Some are more environmentally friendly than others, while some are more expensive to install.
The cost to remove and replace insulation varies widely, but in general the average cost is about $900 for an attic with about 600 square feet of space. It is important to remember that this price does not include the cost of installing new insulation or any other related expenses, such as disposal or roof repairs.
If you are considering replacing your existing insulation, it is best to work with a professional. They can provide a quote for the entire project and ensure that the job is completed safely and effectively. In addition, they can also advise you on the most suitable type of insulation for your home.
Other factors that can influence the cost of removing and replacing insulation include:
Blown insulation – This type of insulation is blown into the attic using a machine. It is more efficient than fiberglass batting, but it may be more difficult to install. It can be a good option for older homes that have old blown insulation that needs to be removed.
Moldy insulation – Old and moldy insulation can be a serious health risk. It can harbor allergens and other pollutants that can damage your indoor air quality. Moldy insulation should be replaced immediately to avoid further damage and to protect your family’s health.
The Essential Role of Electricians in Modern Society
Electricians Fort Worth are the unsung heroes of the modern world, working tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure that our homes, businesses, and communities have access to safe, reliable electricity. From installing wiring and electrical systems to troubleshooting issues and performing maintenance, electricians play a crucial role in powering our daily lives. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the importance of electricians, their training and skills, the diverse career opportunities in the field, and the evolving landscape of electrical work in the 21st century.
The Significance of Electricians:

Electricians are essential to the functioning of modern society. Without their expertise, homes would be without light, businesses would grind to a halt, and essential services would be compromised. Electricians are responsible for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Installing wiring, lighting fixtures, outlets, and circuit breakers in homes, offices, and industrial facilities.
- Troubleshooting electrical issues and diagnosing problems with electrical systems.
- Performing maintenance to ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical installations.
- Upgrading electrical systems to meet changing needs and technological advancements.
- Ensuring compliance with electrical codes, regulations, and safety standards.
In short, electricians are the backbone of our electrical infrastructure, ensuring that electricity flows safely and reliably to power our homes, businesses, and communities.
Skills and Training:
Becoming an electrician requires a combination of technical skills, practical experience, and formal education. Many electricians start their careers by completing an apprenticeship program, which typically lasts four to five years. During this time, apprentices work under the supervision of experienced electricians, gaining hands-on experience and learning the skills necessary to become proficient in the trade.
Apprenticeship programs provide a comprehensive education in electrical theory, practical skills development, and safety protocols. Apprentices learn how to read blueprints, install wiring, troubleshoot electrical issues, and adhere to electrical codes and regulations.
In addition to apprenticeship programs, some electricians pursue formal education through vocational schools, community colleges, or trade schools. These programs offer courses in electrical theory, blueprint reading, wiring techniques, and safety practices, providing students with a solid foundation in the principles of electricity and electrical systems.
Key Skills for Electricians:
- Technical Proficiency: Electricians must have a solid understanding of electrical principles, circuits, and systems. They should be able to read blueprints, schematics, and technical diagrams accurately.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Electrical work often involves troubleshooting complex issues and diagnosing problems. Electricians must have excellent problem-solving skills to identify the root cause of electrical issues and implement appropriate solutions.
- Attention to Detail: Precision and attention to detail are crucial in electrical work, as even small errors can have significant consequences. Electricians must meticulously follow safety protocols, wiring diagrams, and building codes to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
- Safety Awareness: Safety is a top priority in electrical work, given the inherent hazards associated with working with electricity. Electricians must be well-versed in safety protocols, practices, and regulations to prevent accidents, injuries, and electrical hazards.
Career Opportunities:
Electricians have diverse career opportunities available to them across various industries and sectors. Some common career paths for electricians include:
- Residential Electrician: Residential electricians specialize in electrical work for homes, apartments, and other residential properties. They install wiring, lighting fixtures, outlets, and circuit breakers, as well as troubleshoot electrical issues and perform electrical upgrades and renovations.
- Commercial Electrician: Commercial electricians focus on electrical installations and maintenance for commercial buildings, offices, retail stores, and other non-residential properties. They may work on projects ranging from wiring and lighting installations to power distribution and electrical system upgrades.
- Industrial Electrician: Industrial electricians work in industrial settings such as factories, manufacturing plants, and warehouses. They are responsible for maintaining and repairing heavy-duty electrical machinery, equipment, and systems, as well as troubleshooting electrical issues to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency.
- Maintenance Electrician: Maintenance electricians specialize in troubleshooting and repairing electrical issues in various settings, including residential, commercial, and industrial facilities. They perform routine inspections, diagnose electrical problems, and implement corrective measures to ensure the reliability and safety of electrical systems.
The Future of Electrical Work:
The field of electrical work is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changes in regulations, and emerging trends. Electricians must stay updated on the latest developments in the industry to remain competitive and adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
One significant trend shaping the future of electrical work is the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. With growing concerns about climate change and environmental impact, there is a growing demand for energy-efficient electrical systems, renewable energy sources, and green building practices. Electricians with expertise in energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy systems are well-positioned to capitalize on these trends and play a key role in building a more sustainable future.
Another emerging trend is the integration of smart technology and automation into electrical systems. Smart homes, smart buildings, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices are becoming increasingly prevalent, requiring electricians to adapt to new technologies and learn how to install, configure, and maintain connected electrical systems.
Electricians are indispensable professionals who play a vital role in powering our modern world. With their skills, training, and dedication to safety, electricians ensure that our homes, businesses, and industries have access to safe, reliable, and efficient electrical power. Whether it’s wiring a new home, maintaining industrial machinery, or embracing emerging technologies, electricians are the unsung heroes behind the scenes, driving progress and innovation in the field of electrical work. As we look to the future, electricians will continue to be at the forefront of shaping our electrical infrastructure and empowering communities around the globe.
The Crucial Role of Electricians:
Electricians are the backbone of our modern world, responsible for designing, installing, maintaining, and repairing electrical systems. From the moment we flip a light switch to the operation of complex machinery in factories, electricians ensure that electricity flows reliably and safely to power our daily lives.
In residential settings, electricians wire homes, install lighting fixtures, outlets, and circuit breakers, and troubleshoot electrical issues to ensure the safety and functionality of electrical systems. In commercial and industrial environments, their work encompasses a broader spectrum, including wiring for office buildings, factories, warehouses, hospitals, and other facilities, as well as maintaining and repairing complex electrical machinery and equipment.
Skills and Training:
Becoming an electrician requires a combination of technical skills, practical experience, and formal education. Many electricians start their journey through apprenticeship programs, which typically last four to five years. During this time, apprentices work under the guidance of experienced electricians, gaining hands-on experience and learning the intricacies of the trade.
Apprenticeship programs provide a blend of classroom instruction and on-the-job training, covering topics such as electrical theory, blueprint reading, wiring techniques, safety protocols, and local electrical codes and regulations. This comprehensive training equips electricians with the knowledge and skills needed to tackle a wide range of electrical tasks safely and effectively.
In addition to apprenticeship programs, some electricians pursue formal education through vocational schools, community colleges, or trade schools, where they can earn degrees or certifications in electrical technology. These programs offer specialized training in electrical theory, practical skills development, and preparation for licensure or certification exams.
Key Skills for Electricians:
- Technical Proficiency: Electricians must possess a strong understanding of electrical principles, circuits, systems, and components. They should be proficient in reading blueprints, schematics, and technical diagrams to plan and execute electrical installations effectively.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Electrical work often involves troubleshooting complex issues and diagnosing problems. Electricians must have excellent problem-solving skills to identify the root cause of electrical issues and implement appropriate solutions.
- Attention to Detail: Precision and attention to detail are paramount in electrical work, as even small errors can have significant consequences. Electricians must meticulously follow safety protocols, wiring diagrams, and building codes to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
- Safety Awareness: Safety is a top priority in electrical work, given the inherent hazards associated with working with electricity. Electricians must be well-versed in safety protocols, practices, and regulations to prevent accidents, injuries, and electrical hazards.
Career Opportunities:
Electricians have diverse career opportunities available to them across various industries and sectors. Some common career paths for electricians include:
- Residential Electrician: Residential electricians specialize in electrical work for homes, apartments, and other residential properties. They install wiring, lighting fixtures, outlets, and circuit breakers, as well as troubleshoot electrical issues and perform electrical upgrades and renovations.
- Commercial Electrician: Commercial electricians focus on electrical installations and maintenance for commercial buildings, offices, retail stores, and other non-residential properties. They may work on projects ranging from wiring and lighting installations to power distribution and electrical system upgrades.
- Industrial Electrician: Industrial electricians work in industrial settings such as factories, manufacturing plants, and warehouses. They are responsible for maintaining and repairing heavy-duty electrical machinery, equipment, and systems, as well as troubleshooting electrical issues to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency.
- Maintenance Electrician: Maintenance electricians specialize in troubleshooting and repairing electrical issues in various settings, including residential, commercial, and industrial facilities. They perform routine inspections, diagnose electrical problems, and implement corrective measures to ensure the reliability and safety of electrical systems.
The Future of Electrical Work:
The field of electrical work is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changes in regulations, and emerging trends. Electricians must stay updated on the latest developments in the industry to remain competitive and adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
One significant trend shaping the future of electrical work is the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. With growing concerns about climate change and environmental impact, there is a growing demand for energy-efficient electrical systems, renewable energy sources, and green building practices. Electricians with expertise in energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy systems are well-positioned to capitalize on these trends and play a key role in building a more sustainable future.
Another emerging trend is the integration of smart technology and automation into electrical systems. Smart homes, smart buildings, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices are becoming increasingly prevalent, requiring electricians to adapt to new technologies and learn how to install, configure, and maintain connected electrical systems.